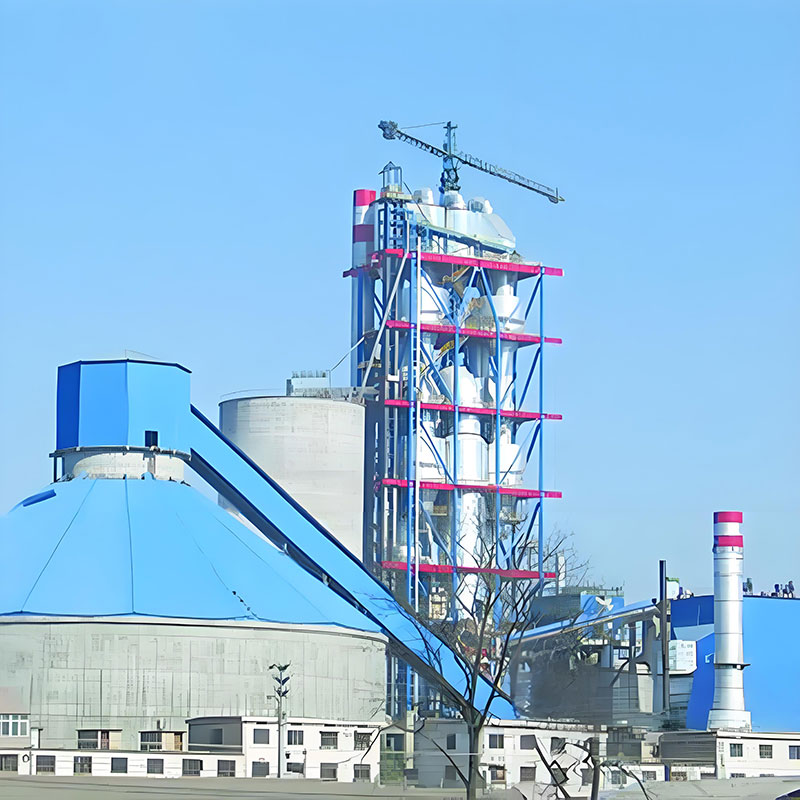
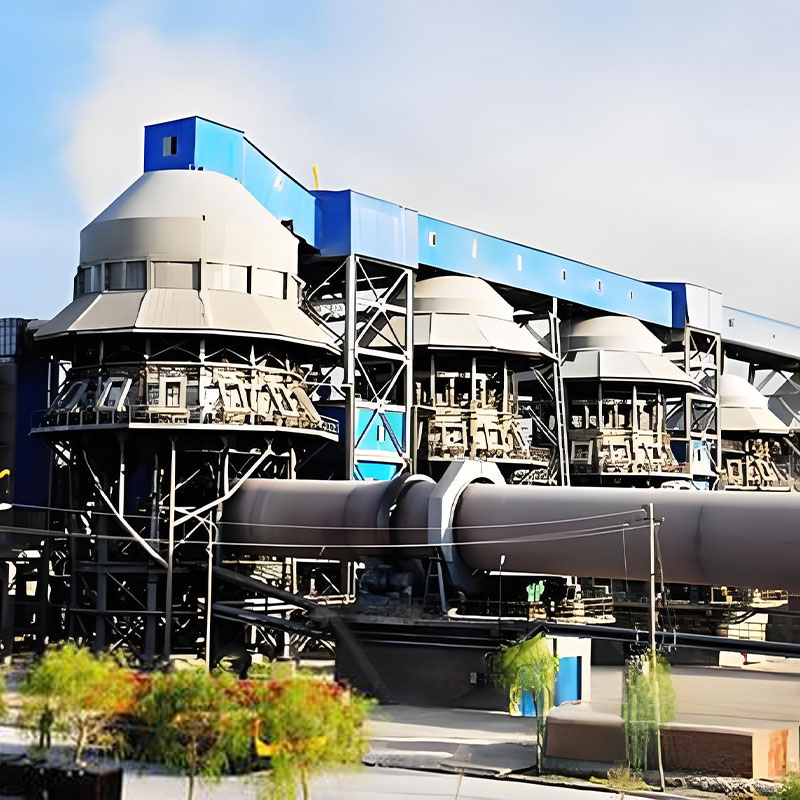
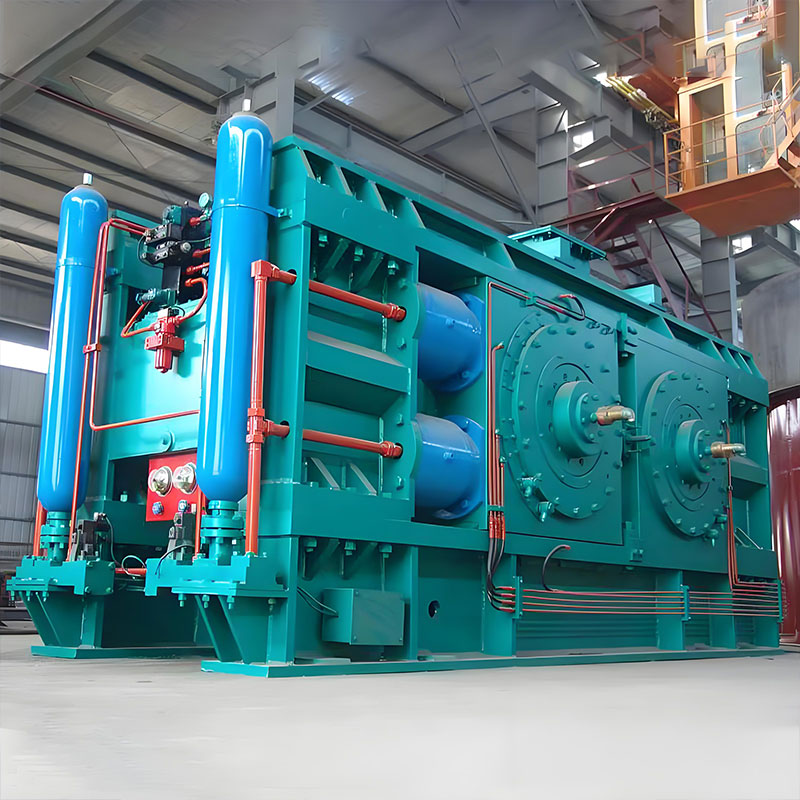
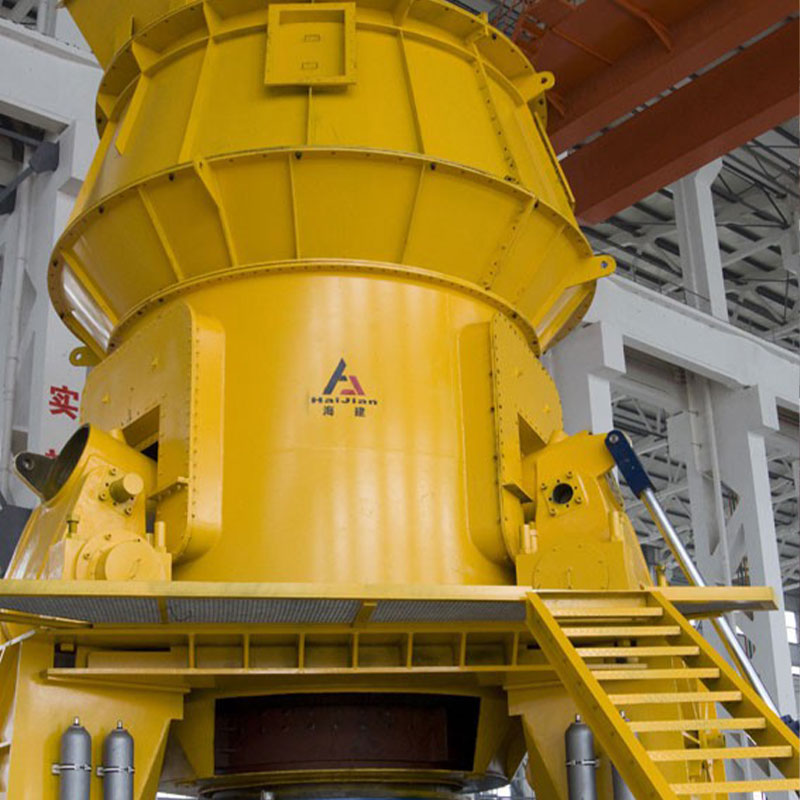
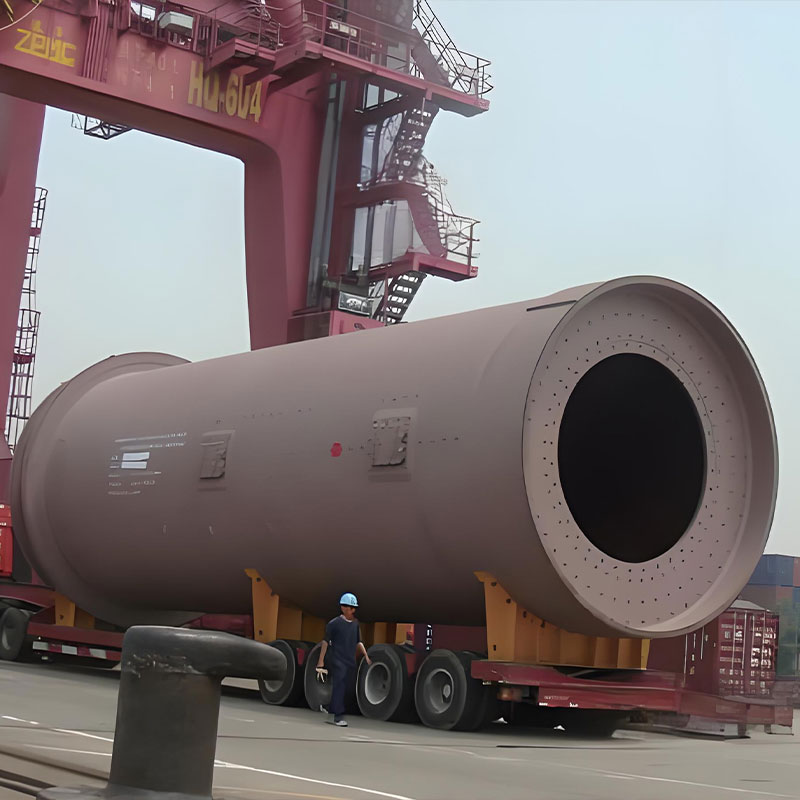
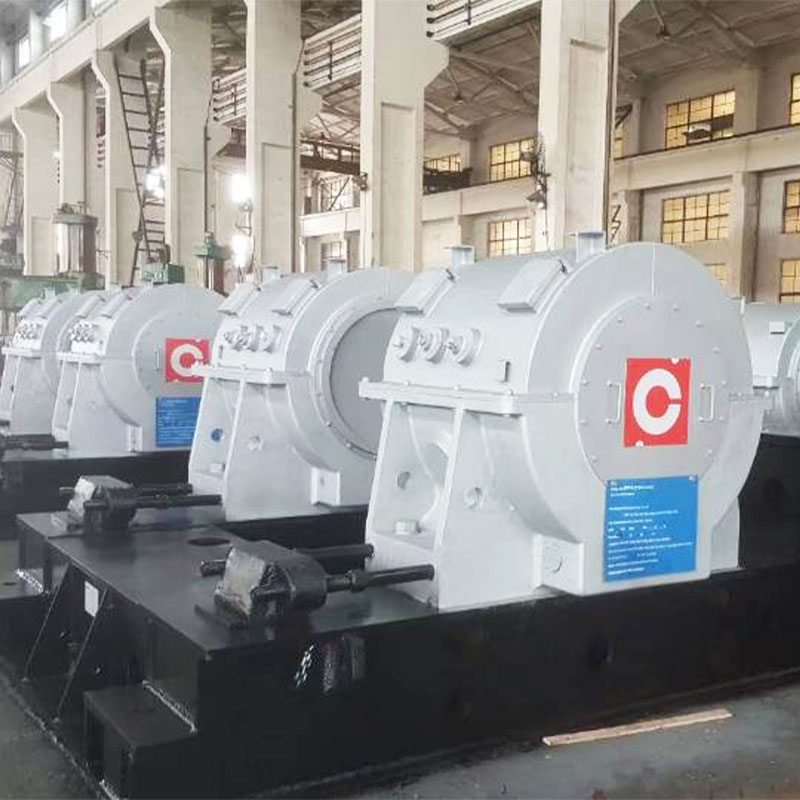
Jiangsu Haijian Co., Ltd is a professional China Heat ex-changer Manufacturers and Heat ex-changer Company. We provide professional cement production equipment, industrial solid waste incineration equipment, and professional equipment for mining and metallurgical applications.We are a major manufacturing enterprise, a key backbone enterprise, and a primary export base for cement, power, environmental protection, and metallurgical and mining equipment in China. The company has the legal rights to independently manage the import and export of its products and is legally authorized to undertake general contracting for foreign projects.
-

Professionalism
-

Quality
-

One stop solution



News Center
News Updates
-
Admin 2026-01-30
Cement Production Line: Is It the Most Efficient Way to Build Modern Infrastructure?
A cement production line is the backbone of large-scale construction projects and urban development. By integrating automated processing, energy-efficient systems, and quality control technologies, modern cement production lines deliver consistent output and stable material performance for global in...Read More -
Admin 2026-01-22
What is a Cement Production Line and How Does It Work?
Cement production is the backbone of the construction industry, providing the essential material used in building everything from houses to highways. But how exactly is cement made, and what role does a cement production line play in this process? In this article, we’ll explore what a cement product...Read More -
Admin 2026-01-16
Is cement production line equipment maintenance difficult?
Many cement plant managers ask: Is cement production line equipment maintenance very complicated? Will it delay production? Actually, as long as a standardized maintenance process is established, daily maintenance is not difficult and can effectively reduce downtime and extend equipment lifespan. Re...Read More
Industry knowledge
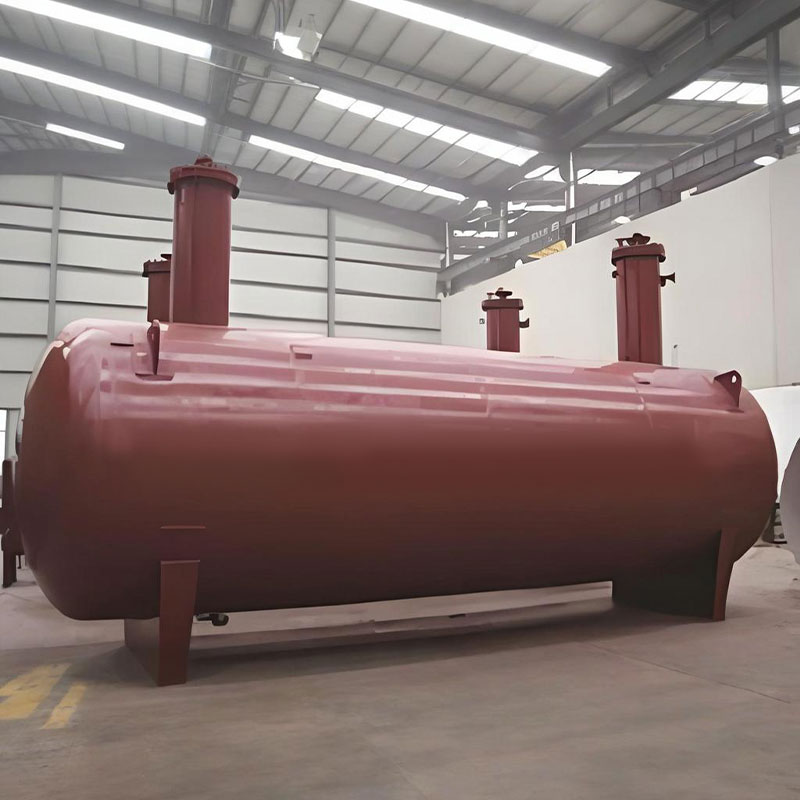
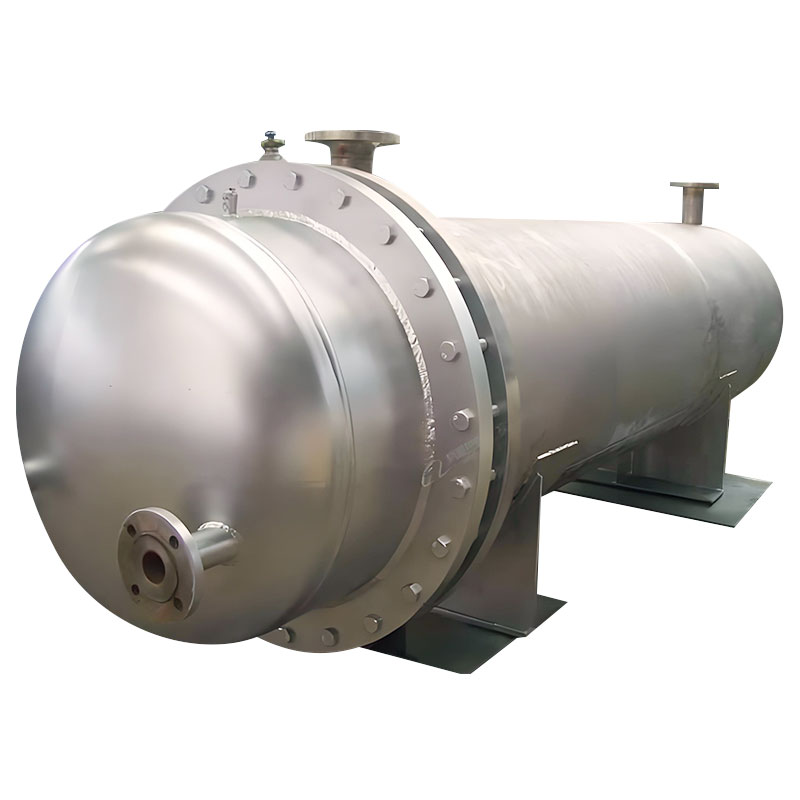
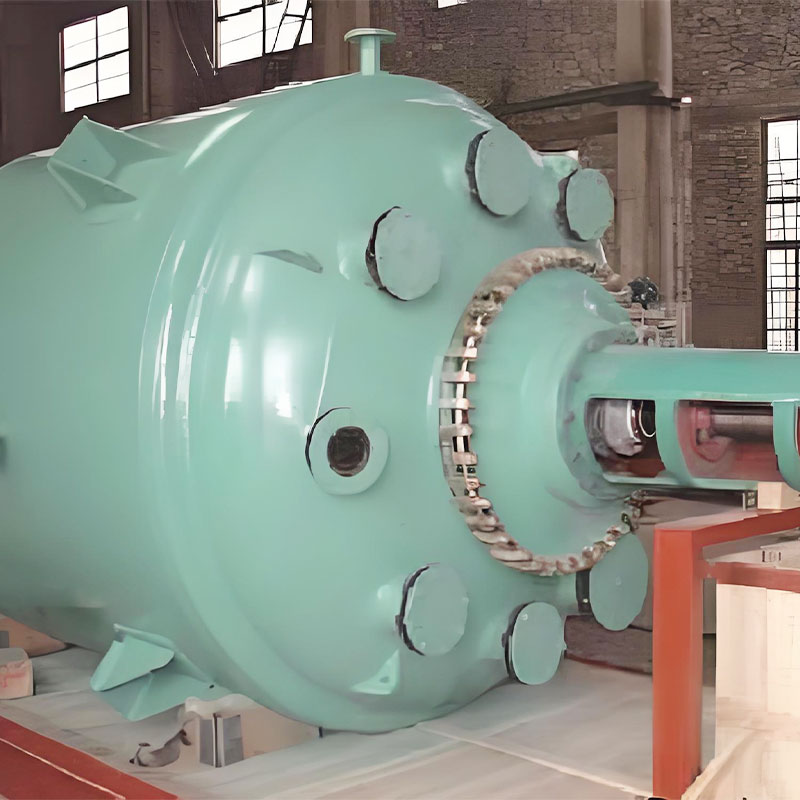
Heat exchangers (also known as heat exchangers) are key devices used to transfer heat between different media. They are widely used in industries such as chemical, power generation, petroleum, pharmaceutical, food processing, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Jiangsu Haijian Co., Ltd. is a professional heat exchanger manufacturer and company. As a "bridge" for energy conversion, heat exchangers continuously promote industrial energy conservation, emission reduction, and sustainable development through continuously upgraded material applications and heat transfer optimization. Their main functions include:
Heat recovery: For example, waste heat utilization (shell-and-tube waste heat vessels) reduces energy consumption.
Cooling/heating: Regulating media temperature through chillers, condensers, and evaporators.
Process control: Maintaining constant temperature conditions in sterilizers and reaction systems.
Energy conservation and environmental protection: Reducing waste heat emissions, improving energy efficiency, and contributing to sustainable development.
Operating Principle
Heat exchangers operate based on the principles of heat conduction and convection, transferring heat between hot and cold media through solid walls or direct contact. Key types include:
Shell-and-tube heat exchangers: The hot and cold fluids flow in the tube side and shell side, respectively, and are suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments (such as the petrochemical industry). Plate heat exchangers: Corrugated plates create flow channels, resulting in high heat transfer efficiency and easy disassembly and cleaning (e.g., in the food industry).
Fin-type heat exchangers: Fins enhance heat transfer and are commonly used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
Direct contact heat exchangers: Direct mixing of hot and cold media for heat exchange (e.g., in cooling towers).
Advantages and Features
Efficient heat transfer: Optimized flow channel design (e.g., spiral baffles and turbulence enhancement structures) improves heat transfer coefficients.
Upgraded materials: Corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., titanium alloy, graphite, and composite materials) are used to extend service life.
Compact structure: Modular design saves space. For example, plate heat exchangers can achieve 3-5 times the heat transfer area per unit volume of shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
Intelligent control: Integrated temperature and flow sensors enable automated adjustments (e.g., AI-powered optimization of heat exchange networks).
Post-maintenance and optimization
Regular cleaning: Prevents scaling and clogging (e.g., chemical cleaning or mechanical flushing).
Corrosion inspection: Monitors welds and seals to prevent leakage.
Energy efficiency monitoring: Evaluates heat exchange efficiency through thermal imaging or pressure drop analysis.
Upgrade and transformation: Use coating technology (such as nano-coating) to reduce dirt deposition.

 English
English  русский
русский  Español
Español 


















