What factors affect the quality stability of a cement production line?
In today's increasingly competitive cement industry, the stability of cement quality has become a key factor for enterprises to survive in the market. For cement production lines, quality is not determined by a single link, but involves multiple factors such as raw materials, equipment, processes, operations, and testing. Only through system optimization and full-process control can cement products with stable performance, reliable strength, and compliance with standards be produced. So, what factors affect the quality stability of a cement production line?
1. Differences in Raw Material Quality
Cement quality depends primarily on raw materials. The main raw materials include limestone, clay, and iron-based corrective materials, and fluctuations in their chemical composition directly affect clinker quality.
(1) Uneven Limestone Composition
Excessive fluctuations in the CaO content and silicate ratio of limestone can lead to difficulties in clinker firing, thus affecting strength and stability.
(2) Changes in Raw Material Humidity
In rainy seasons or high-humidity environments, increased raw material humidity can affect grinding efficiency and the uniformity of raw meal composition.
(3) Unstable Impurity Content
For example, excessively high MgO content (exceeding a certain proportion) can affect the volume stability of cement, leading to end-product quality problems. Therefore, the selection, homogenization, storage, and online monitoring of raw materials are crucial for stable quality.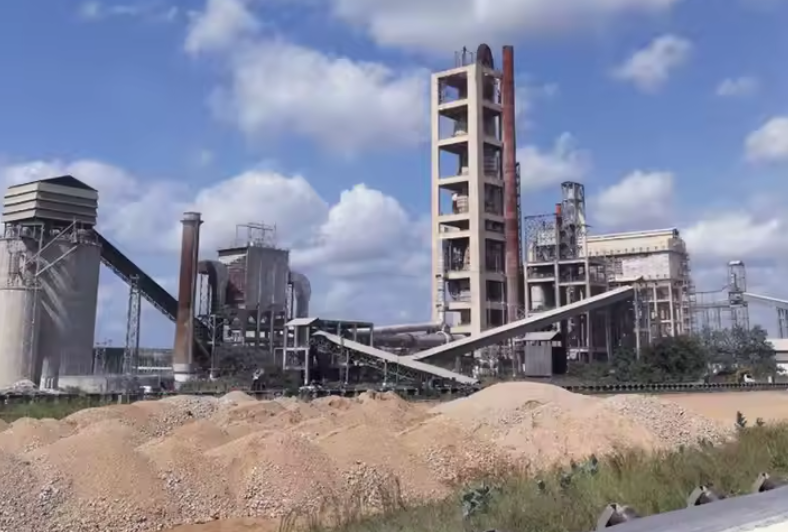
2. Grinding System Efficiency Affects Fineness and Particle Distribution
Raw material grinding and cement grinding are key steps determining the fineness and uniformity of product particles.
(1) Poor Grinding Equipment Condition
Wear of mill liners and grinding rollers can lead to a decrease in grinding capacity and unstable product fineness.
(2) Fluctuations in Classifier Efficiency
Unstable classifier speed or internal wear can lead to unreasonable particle distribution, affecting cement setting performance and strength.
(3) Large Variations in Material Circulation Load
Excessive or insufficient load can affect energy consumption, fineness, and the controllability of final cement quality.
Stable operation and timely maintenance of the grinding system are fundamental guarantees for stable cement quality.
3. Stability of the Firing System Determines Clinker Quality
Clinker is the core of cement quality, and the key factor affecting its performance is the firing system, including the preheater, decomposition furnace, and rotary kiln.
(1) Unstable Kiln Temperature
Excessively high temperature can lead to over-burning of clinker, while excessively low temperature can lead to under-burning, thus affecting the mineral composition ratio.
(2) Coal Quality Fluctuations
Excessive fluctuations in fuel ash and volatile matter directly cause unstable heat distribution within the kiln.
(3) Uneven Feeding
Fluctuations in feeding cause kiln condition fluctuations, disrupting the stable clinker formation process.
(4) Poor Rotary Kiln Mechanical Condition
Wear on rollers and tires can cause kiln movement, affecting stable firing.
A stable firing regime is crucial for producing high-strength, high-quality cement.
4. Clinker Cooling and Storage Affect Final Performance
The clinker cooling rate affects mineral phase formation; for example, rapid cooling can form more active mineral phases, increasing cement strength.
Poor cooler efficiency leads to coarse clinker grains. Overheated clinker entering the storage silo can cause agglomeration. Unstable cooling airflow leads to fluctuations in cooling effect. The cooling process, seemingly simple, has a profound impact on quality.
5. The Quality of Additives and Blends Affects the Overall Performance of Cement
Modern cement often uses blends such as fly ash and slag. Their activity, fineness, and moisture content all affect cement performance.
Insufficient blend activity reduces cement strength; excessive moisture content affects grinding efficiency; excessive impurities affect cement stability.
Furthermore, improper control of gypsum addition can cause abnormal setting time.
The factors affecting the quality stability of a cement production line are multifaceted, from raw materials to grinding, from firing to storage, and then to automation systems and operational management. Each link can potentially become a source of instability. Only through a strict quality control system, advanced equipment, precise process management, and a professional operating team can truly stable and reliable cement quality be achieved, giving enterprises a competitive edge.
News Category
Recommended Products
It is focused on the overall solution of dry bulk material port transfer system,
research and development, manufacturing, and service
- Product Category
- >Cement production line
- >Environment protection
- >Metallurgical and mining equipment
- >Pressure Vessel
- Quick Links
- >Products
- >Company
- >Equipments
- >Solutions
- >Services
- >News
- >Contact
- Contact us
-
-
 Call us for support+86 13584702563
Call us for support+86 13584702563 -
 Call us for supporthaijian@haijianstock.com
Call us for supporthaijian@haijianstock.com -
 No. 198, Shuanglou Road, Qutang Town, Haian County, Jiangsu Province
No. 198, Shuanglou Road, Qutang Town, Haian County, Jiangsu Province
-

 English
English  русский
русский  Español
Español 









